|
CPU / Microprocessor
 There are three aspects to consider when evaluating a microprocessor: The processor family, the number of threads and the speed of the processor.
These days the Intel microprocessors will perform about 1/3 more work than an AMD microprocessor
operating at the same GHz speed and with the same number of cores. Intel releases new processors every 12-18 months but some of these releases are just minor updates and in some respects may
have some disadvantages when compared to its predecessor. For example, the “Haswell” series was only a slight improvement in performance over the “Ivy Bridge”
but it runs much hotter when working hard and this heat triggers a thermal throttling effect that slows down the processor to help control the
overheating problem. The
thermal throttling renders the performance inferior to the Ivy Bridge predecessor
in many situations unless you invest in much better cooling for the processor.
However, even with the best cooling the smaller
size of the Haswell makes it hard to keep cool. You should
consider both the Ivy Bridge and the Haswell family of Intel microprocessors when making your buying decision. There are three aspects to consider when evaluating a microprocessor: The processor family, the number of threads and the speed of the processor.
These days the Intel microprocessors will perform about 1/3 more work than an AMD microprocessor
operating at the same GHz speed and with the same number of cores. Intel releases new processors every 12-18 months but some of these releases are just minor updates and in some respects may
have some disadvantages when compared to its predecessor. For example, the “Haswell” series was only a slight improvement in performance over the “Ivy Bridge”
but it runs much hotter when working hard and this heat triggers a thermal throttling effect that slows down the processor to help control the
overheating problem. The
thermal throttling renders the performance inferior to the Ivy Bridge predecessor
in many situations unless you invest in much better cooling for the processor.
However, even with the best cooling the smaller
size of the Haswell makes it hard to keep cool. You should
consider both the Ivy Bridge and the Haswell family of Intel microprocessors when making your buying decision.
The second consideration is the number of threads:
microprocessors these days have multiple “cores” and
each core can process any type of instruction such that a four core processor can process four simultaneous instructions. The multiple core
function has advantages in speeding up how long it takes to perform calculations, but only if the software is written in such a way as to
take advantage of multiple cores. When a program is written in multiple “threads” then each thread can use a different core to get the job
done. While this is changing, most trading platforms will only operate in a single thread and can therefore only use one core.
 If you are using a single threaded trading program then upgrading to a processor that can handle more threads will not help you at all. We will
discuss more about this later. The difference between the higher end Intel i5 and i7 series of processors is that the cores in the i7 series
use “hyperthreading”, which allows math calculations to be handled separately from other calculations thus increasing the number of
possible threads. In a four core i7 processor there are eight possible threads: four for math and four for non-math calculations. This is helpful for
those few programs that can use the hyperthreading feature effectively. Any program can make use of a microprocessor with a faster GHz speed, even if
it uses just one thread. More threads may be helpful but it should not
normally be at the sacrifice of faster processing speed.
All Intel microprocessors produced in recent years have what is called a "Turbo
Boost" mode which allows
it to speed up when the workload is heavy. The turbo mode is an important boost in processing power that
traders will want to make use of during times when the trading volume is heavy. The turbo feature will not kick
in for more than a few seconds if the microprocessor does not have excellent
cooling,
which is not the case on most low
cost computers. Also, to get the turbo mode to reach its full speed for more than a few
seconds you need to have one
of the better Intel motherboard chipsets (more on that next).
Main Board / Motherboard
Mass produced computers that are commonly sold by the major computer brands have reduced performance after many years of intense cost cutting
from a very price competitive environment. They often combine newer processors with low end and sometimes out dated motherboard chipsets. Most
computer buyers are unaware of what a motherboard chipset is and how important it is in getting the full measure of use out of a microprocessor.
The motherboard chipset is a set of "chips" (integrated circuits) that that manages the data flow between the processor, and
peripherals (video cards, sound, internet, etc.). Lower
cost Intel chipsets like the B75, Z75, H77, Q77, B85, H81, H87, and Q87 will
generally not sustain the turbo mode of the Intel processor for more than a few seconds. If you want to get full access to the power
boost from the turbo mode you will need one of the high end Intel chipsets: Z77, Z87, X79.
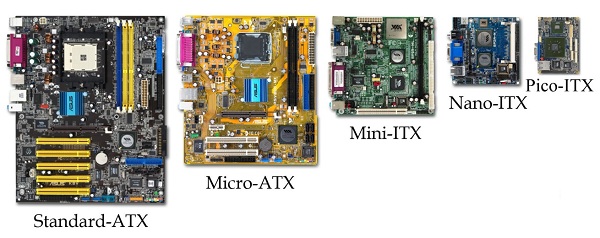
The size of the motherboard on the computer will have a large effect on what features you will be allowed to have. Inexpensive computers
will have the smallest motherboards with the fewest features:
Cooling
 Trading computers typically work much harder than normal computers and should have a superior cooling system for the entire computer but with special
attention given to the processor. You want your computer's case to be large enough to allow air to freely pass through it and cool all
the components. You also need enough fans to keep the air moving
everywhere to avoid hot spots. Trading computers typically work much harder than normal computers and should have a superior cooling system for the entire computer but with special
attention given to the processor. You want your computer's case to be large enough to allow air to freely pass through it and cool all
the components. You also need enough fans to keep the air moving
everywhere to avoid hot spots.
To cool the microprocessor you need much better cooler than the free one that comes from Intel with the processor. The free Intel coolers are barely strong
enough to keep the newer processors from getting too hot
and will greatly limit the turbo boost mode. Liquid cooling systems are more effective but much less reliable than air coolers. We prefer not to use
the
small pre-packaged liquid coolers due to
their poor reliability over the life of the
computer (we tried them all). Some air coolers, like the Arctic Breeze and Arctic Storm units
used on
Falcon trading computers outperform most of the liquid cooling units on the market
today while also leveraging the high reliability of air cooling. The Falcon F-52X
custom liquid cooling option is handmade and very reliable because it uses commercial
components rated at over 50,000 hours and redundant cooling fans.
Memory
When we
at Falcon Trading Computers first began building trading computers
over a decade ago you could get by with one gigabyte of memory. Back
then 300-400MB was enough for the windows operating system and 200-300MB for your trading software. These days the computer won’t even boot up with only one
gigabyte of memory. The lowest amount of memory we
at Falcon offer is 8 gigabytes but to you
may want to get more to accommodate possible
future increases in memory usage by future trading
software version releases.
How fast the memory provides information
to the processor is a mix of the speed of the memory in megahertz or gigahertz (“clock speed”) and the latency of the memory.
Latency is a measure of the internal task speed of the memory. If the task timings of the memory in your computer are 7-7-7-22 and the clock speed is
1.33GHz then that is the same overall speed as a clock speed of 1.67GHz and timings of 9-9-9-24 so faster clock speed memory is not better memory if the
timings are slower. It is not uncommon to see timings of 11-11-11-28 on memory these days with a clock speed of 1.6GHz, which yields a much slower overall
performance than 7-7-7-22 and a clock of 1.33GHz. However, the higher GHz memory will stress the processor more so it is better to go with a lower memory
clock speed that is offset by faster memory timings.

Using high reliability memory is important
in order to avoid losses due to computer malfunctions when you are trading. The memory chips should be manufactured in
factories that adhere to the highest clean room standards and use the best manufacturing processes. If there was a 1 in a billion chance of an error then you would
have 16 errors in a 16GB system. To achieve good reliability over the life of the computer requires an extraordinary level of reliability.
We have used
nearly every memory manufacturer that exists at one time or another and we buy over
5,000 sticks of memory each year. It is our opinion that
only Hynix memory chips
deliver the kind of performance and reliability that is needed by traders. Hynix is the second largest memory manufacturer in the world. They build memory that is
used in high quality products (most iPhones, iPads, MacBook Pro, high end Android cell phones, etc.) and mission critical business and government computers (IBM
System X, Dell servers, and HP servers).
Power Supply
The power supply
is usually the most overlooked element in buying a computer but it is a very important consideration. When a computer
fails it is often a deficiency in the power supply that directly or indirectly led to the failure. Power supplies use a component
called a "capacitor" to smooth out the DC current that goes to your computer's motherboard, and other components.
 Capacitors gradually degrade over time; they degrade faster with elevated temperatures and
elevated workloads. Larger wattage power supplies have higher ratings for their capacitors which helps them to last longer
in lighter duty applications. If the computer draws 250 watts normally then a
power supply of at least 500 watts would be the smallest one to consider if you want it to last a long time but a power supply of
more than 600 watts would be much better. Also, the initial power surge when the computer starts requires a larger power
supply. The computer will not draw more power with a larger power supply, it will just last a lot longer.
After wattage, then it is the maximum current that can be supplied by the 12 volt circuit that is critical in distinguishing a good power
supply from a low quality power supply. 12 volt circuits are sometimes divided into multiple circuits called “rails”. For a trading
computer I would recommend no less than 38 amps for the 12 volt circuit and no less than 20 amps for each rail if there is more than
one rail. It is preferred to have more than 45 amps total capacity on the 12 volt circuit because many of the better processors and
video cards have a high instant starting current which may trigger the overload safety device when you try to start your computer.
Graphics Cards
 Your trading software
vendor will often not specify a particular
graphics card (a.k.a video card) requirement for a computer in either the
minimum system requirements or the recommended system requirements. An exception to this is ThinkOrSwim which has
some very powerful graphics cards listed in the
recommended system requirements. Since the vast majority of computers sold today have poor video cards it is
easy for them to just say your computer is not
good enough. Investing in a good video card can improve
the performance of your computer when trading. However, buying a big gaming card is unlikely to help you
much since those video cards focus on 3D gaming technology not the 2D technology you need for trading. Your trading software
vendor will often not specify a particular
graphics card (a.k.a video card) requirement for a computer in either the
minimum system requirements or the recommended system requirements. An exception to this is ThinkOrSwim which has
some very powerful graphics cards listed in the
recommended system requirements. Since the vast majority of computers sold today have poor video cards it is
easy for them to just say your computer is not
good enough. Investing in a good video card can improve
the performance of your computer when trading. However, buying a big gaming card is unlikely to help you
much since those video cards focus on 3D gaming technology not the 2D technology you need for trading.
The AMD based graphics cards are more likely to leave "trails" when you move windows around than the NVIDIA based cards.
The trails go away when you are done moving
the windows.
Selection of video cards is important to hit that sweet spot where you maximize 2D performance. The middle
of the product line is usually the right spot to look (not too cheap and not to expensive).
Graphics cards have several possible types of connections to monitors: DVI, Dual-Link DVI, Display Port, mini-Display
Port, HDMI, mini-HDMI and VGA. Some, but not all, can be converted from one type to another with an adapter.
More on this below. You will
need an individual connection on the back of your computer for each monitor. Monitors with a resolution greater than
1920x1200 are only supported by some graphics cards.
Hard Drives
Hard Drives will have a powerful effect on your trading computer experience. The new solid state hard drives (SSD) are very fast. After you get used
to the new SSD’s you will not want to go back to the slow archaic mechanical hard drives.
Keep in mind that not all SSD’s have the same speed or reliability.
Solid state hard drives are very sophisticated devices with little computers inside that regulate their performance and prevent them from wearing
out too soon. Any one memory location in an SSD has a limited number of times that it can be written to before it stops working; so the job of this
little computer (which we will call the “controller”) is to rotate usage of every memory location to even out the wear. Additionally, any one
location has a limited number of times it can be read before the electrical charge stored there is too weak to read anymore so it must be recharged
it before it reaches that limit. The erasing process is also complex and must be managed well to prevent severe degradation of drive performance (a
problem called “write amplification”) while avoiding too many writes that will cause premature drive wear out.
Internet
Internet speed is often a major concern of traders. However, speed is often confused with bandwidth. A 10 gigabit Internet connection is not slower
than a 50 gigabit connection, it just has more bandwidth. It is like driving on an interstate highway: Bandwidth is the number of lanes of traffic
and speed is the speed that the vehicles are
traveling. A bandwidth of 10 gigabits or more is plenty. Speed is hard for the buyer to control in the purchase process
because it is primarily dependent on how traffic is routed by the Internet Service Provider (ISP). If you can ping your data provider’s servers
then you
can check the delay time. Most ISP’s route Internet traffic based on cost rather than speed. I have seen Internet traffic from northern Colorado routed
through Los Angeles on the way to Chicago rather than through Denver in order to save money. Using the “ping” command will help you look into this
but the use of ping is not in our scope here. You can find out how to use ping on various Internet websites. Unless you like to scalp
trades on a very small time frame your Internet speed is not worth worrying about because the total time involved is much less than a second.
If your computer has two Internet connections then it is natural to assume that you can plug in two different Internet sources to it and if one goes
down then the other will take over. This is assumption is false. The Windows operating system can see both Internet connections but it will only use
one of them because it only has the ability to use one Internet Gateway IP address. You can use the second one for a safer internal local network that
that is not exposed to the risk of the Internet.
Wireless connections are Ok if you cannot route an Ethernet cable to your computer but they are more prone to problems from security and channel
conflicts (two devices using the same wireless channel).
Noise
The amount of noise that your computer makes depends on the number of fans, size of the fans, speed of the fans, and blade design of the fans. Small
fans usually make more noise than large fans. Fans that turn faster than 1,200rpm will make more than those that are slower. Fans that have an unusual
blade design usually make less noise than conventional fan blades. The use of proper sound proofing materials is also a way to reduce noise.
Backups
Backing up your computer is a good idea if you don’t want to lose
data
someday. Cleaning out a virus or fixing registry corruption is
an additional possibility if you have good
image backups. The best backup software will back up the entire hard drive
(make an image),
not just your data, such that you could install a brand new drive and restore it from the
image backup for a 100% recovery.
Warranty
Not all warranties are the same. A computer warranty differs from other types of warranty in that you have the possibility
of receiving a very valuable service: technical support. High quality technical support will save you a lot of money since your alternative is to go to
a repair shop and pay a hefty charge to get it done there. Falcon trading computers offer the highest level of technical support in the industry including
help with configuring and optimizing your trading software as well as virus removal.
If your warranty is the mail-in type that most trading computer companies have (Falcon trading computers are the exception) then you will need to be able to
go for an extended period of time as it is shipped each way by ground and spends some time in the shop. The down time will likely be at least a few weeks
and often longer while they send in the broken part to the manufacturer to be repaired or replaced. What you should get is a warranty that will send
the part to you quickly and a technician will arrive at about the same time to perform the work.
|


